
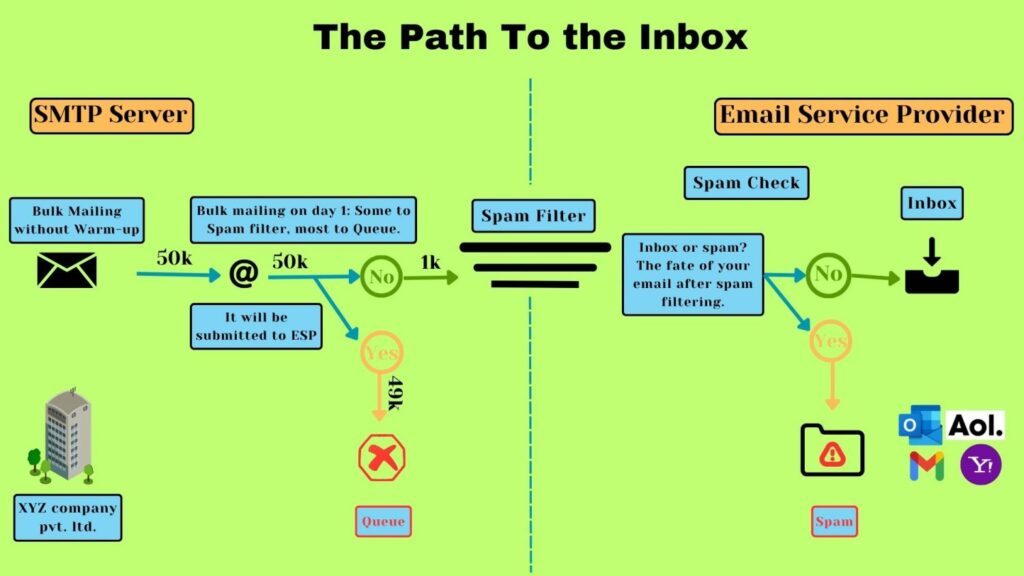
When you start bulk mailing to other ISPs, there is a risk of being flagged as spam. ISPs have strict filtering systems in place to protect their users from unsolicited or unwanted emails. If your emails are marked as spam by recipients or identified as suspicious by the ISP, it can harm your reputation, making it difficult for your future emails to reach the inbox.
ISPs employ advanced algorithms to filter and detect spam. Bulk mailing from unfamiliar or questionable sources may be more likely to be filtered and sent to the spam folder instead of the inbox. This reduces the visibility and effectiveness of your email campaigns, as recipients are less likely to see or engage with emails in their spam folders.
Definition of bulk mailing:
Bulk mailing allows businesses and organizations to reach a wide audience and deliver their message efficiently and cost-effectively. It is commonly used for email marketing campaigns, newsletters, promotional offers, or other mass communication purposes. In bulk mail, the content of the message remains the same for each recipient, with minor personalization or customization, such as addressing each recipient by their name. The goal is to deliver information, promote products or services, or engage with a large number of individuals or subscribers. Bulk mailing refers to the practice of sending a large volume of identical or similar messages to multiple recipients simultaneously.
Key features of bulk mail:
- Cost-effectiveness: Bulk mail can be a cost-effective marketing strategy compared to individualized communication methods.
- Standardized content: The core message remains consistent across all recipients, though minor personalization may be included.
- Mass distribution: Bulk mail involves sending messages to a large number of recipients simultaneously.
- Efficiency: It allows for streamlined and automated sending processes, saving time and effort.
Overall, bulk mail serves as a means to efficiently communicate with a large audience, enabling businesses and organizations to convey their message, build customer relationships, and achieve their marketing objectives on a broader scale.
Then how to send bulk mail?

1. Building and Maintaining a Good Sender Reputation:
Among the prominent ISPs, Gmail has Google Postmaster, which tracks the domain & IP reputation, while Hotmail has SNDS, which tracks the IP reputation.
There are special tools that can help you check your email sender reputation.
Now, if your sender reputation has a bad score, then you can follow these steps to have a good sender reputation:
- Identify which blocklists you’re on
- Delist your IP address
- Set up an SSL/TLS certificate
- Warm up the IP
For manually IP warming method, you can refer to our article on “Secret of IP warming – Plans, Schedule, Strategy & Pitfalls.“
For automated IP warming, there are a few tools which we recommend:
- Mailwarm is a dedicated email warm-up tool. The email warm-up process by Mailwarm is very simple.
- Auto-Warmer is an email warm-up tool by Quickmail. The tool automatically responds to some of your emails. It’s done with real people’s accounts.
- Warmup Inbox is an email warming service. It’s integrated with many email clients, such as Gmail and Outlook 365, Yahoo Mail, Amazon SES, Mailgun, Sendgrid, SMTP, Sendpost, Microsoft 365, Zoho, and Google Workspace.
For more in-depth knowledge, read our article on “Warming up IP? Know the IP reputation with these tools.”
2. Improving Deliverability Rates:
Enhancing deliverability requires adhering to best practices for email content and design, such as optimizing for mobile devices and avoiding spam trigger words.
Additionally, maintaining a clean and engaged email list, regularly removing inactive subscribers, and conducting testing and optimization experiments can significantly improve deliverability rates.
There are several Email Deliverability Testing Tools available that can help you analyze and improve your email deliverability.
- Litmus is a popular email testing and analytics platform. It provides a suite of tools to test and track email campaigns across different devices, email clients, and spam filters. You can preview how your emails appear in various inboxes and identify potential issues that might affect deliverability.
- Email on Acid offers a comprehensive email testing platform. It allows you to preview and test your emails across multiple clients, devices, and spam filters. You can identify any issues related to blacklisted words, rendering, links, images, and more.
- GlockApps provides comprehensive email testing and monitoring services. It allows you to test your emails against various spam filters, email clients, and ISPs. You can identify issues related to blacklisted words, HTML rendering, inbox placement, and more.
For more in-depth knowledge, read our article on “Avoid Email Delivery Pitfalls: Blacklisted Words Unveiled.“
3. Ensuring Compliance and Legal Compliance:
Test and Validate Email Templates: Test your email templates to ensure they comply with email client requirements and display correctly across different devices and platforms.
Keep Records of Consent: Maintain records of consent obtained from recipients, including the date, time, and method of consent. These records can serve as evidence of compliance in case of any legal inquiries or audits.
Monitor and Handle Complaints: Monitor and promptly address any complaints received from recipients. Provide clear channels for recipients to report issues or concerns.
Regularly Update and Manage Mailing Lists: Regularly review and update your mailing lists to ensure accuracy and relevance. Remove inactive or unengaged subscribers to maintain a healthy list.
Provide Clear Opt-Out Options: Include clear and conspicuous opt-out mechanisms in your emails. Allow recipients to easily unsubscribe from your mailing list.
Maintain Proper Sender Identification: Use accurate and identifiable sender information in your email headers. Include a valid physical mailing address and a recognizable sender name or company name.
Understand Anti-Spam Laws and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the anti-spam laws and regulations applicable to your jurisdiction, such as the CAN-SPAM Act in the United States or the GDPR in the European Union.
Honor Privacy and Data Protection Laws: Comply with relevant data protection laws, such as the GDPR. Safeguard personal data collected from recipients and ensure it is handled securely and used only for the intended purposes.
4. Efficient Resource Management:
Optimize Email Content and Attachments: Optimize your email content, including images and attachments, to minimize the impact on server resources.
Assess Infrastructure Needs: Evaluate your current infrastructure and determine if it can handle the volume of emails you plan to send. Consider factors like server capacity, storage requirements, and network bandwidth.
Regularly Clean and Maintain Databases: Periodically clean and update your recipient databases to remove invalid or inactive email addresses.
Monitor and Optimize Costs: Evaluate the pricing structure of your ESP and ensure it aligns with your sending volume and budget.
Monitor Performance Metrics: Regularly monitor key performance metrics like email sending rates, bounce rates, and response times. Analyze the data to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
Implement Load Balancing: Distribute the email sending load across multiple servers or IP addresses to avoid overloading a single resource.
Choose the Right Email Service Provider (ESP): Select an ESP that offers robust infrastructure and scalability options. Ensure they have the capacity to handle your email volume without compromising deliverability.
Optimize Email Delivery Speed: Streamline your email delivery process to maximize efficiency. Minimize delays by optimizing your email sending mechanism, including SMTP settings and email queue management.
Implement Email Queuing and Throttling: Utilize email queuing mechanisms to manage the flow of outgoing emails. Implement email throttling techniques to control the rate at which emails are sent.
Understanding the Challenges and Risks:

Sending bulk mail comes with its own set of challenges and risks that need to be understood and addressed. It is crucial to be aware of these factors to ensure successful email campaigns and maintain a positive sender reputation.
The Pros and Cons of Sending Bulk Mail: Sending bulk mail can be an effective strategy for reaching a large audience with your message. However, it also comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons of sending bulk mail:
- Deliverability Issues: ESPs employ sophisticated filtering systems to protect users from spam and unwanted emails. Bulk mail may face challenges in bypassing these filters and reaching the recipients’ inboxes. Factors like content quality, sender reputation, and engagement rates can impact deliverability.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Compliance with anti-spam laws and regulations is essential when sending bulk mail. Failure to comply with these laws can lead to legal consequences, reputation damage, and deliverability issues. Obtaining proper consent from recipients and adhering to data protection laws are critical considerations.
- Reputation Management: Bulk mail can have a significant impact on sender reputation. Maintaining a good reputation is crucial for successful email delivery. However, sending bulk mail increases the risk of being flagged as spam or having a poor sender reputation.
- Resource Management and Costs: Sending bulk mail requires significant resources, including infrastructure, server capacity, and email delivery services. Scaling up to accommodate large volumes of emails can incur additional costs. Proper resource management and budgeting are necessary to ensure efficient operations.
Pros:
- Personalization options: Many bulk mail platforms offer features that allow you to personalize your messages, such as addressing recipients by their names or tailoring content based on their preferences.
- Wide reach: By sending bulk mail, you can reach a wide audience and increase brand visibility. It provides an opportunity to engage with potential customers, generate leads, and promote your products or services to a broader market.
- Efficient communication: Bulk mail enables you to communicate important information, updates, promotions, or announcements to a large group of people simultaneously.
- Cost-effective: Bulk mail allows you to send messages to a large number of recipients at a relatively low cost per contact. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with limited marketing budgets.
Cons:
- Unsubscribes and complaints: Sending bulk mail runs the risk of recipients unsubscribing from your mailing list or filing complaints if they perceive your messages as unwanted or irrelevant.
- Risk of being marked as spam: Sending bulk mail increases the risk of your messages being flagged as spam, especially if you do not adhere to proper email marketing practices. This can negatively impact your deliverability and brand reputation.
- Compliance challenges: Bulk mail must comply with anti-spam regulations, such as the CAN-SPAM Act and GDPR. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to legal consequences and damage your brand’s reputation.
- Resource-intensive: Sending bulk mail requires adequate resources, including email infrastructure, software, and staff to manage campaigns effectively.
- Managing large data sets: Handling and managing large volumes of recipient data can be challenging. It requires effective list management, segmentation, and maintaining accurate contact information to ensure targeted and relevant communications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, unlimited bulk mailing can be a powerful tool for businesses to reach a large audience efficiently. However, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. By following best practices and leveraging the right resources, you can make the most of bulk mailing while minimizing the risks and maximizing the benefits.
